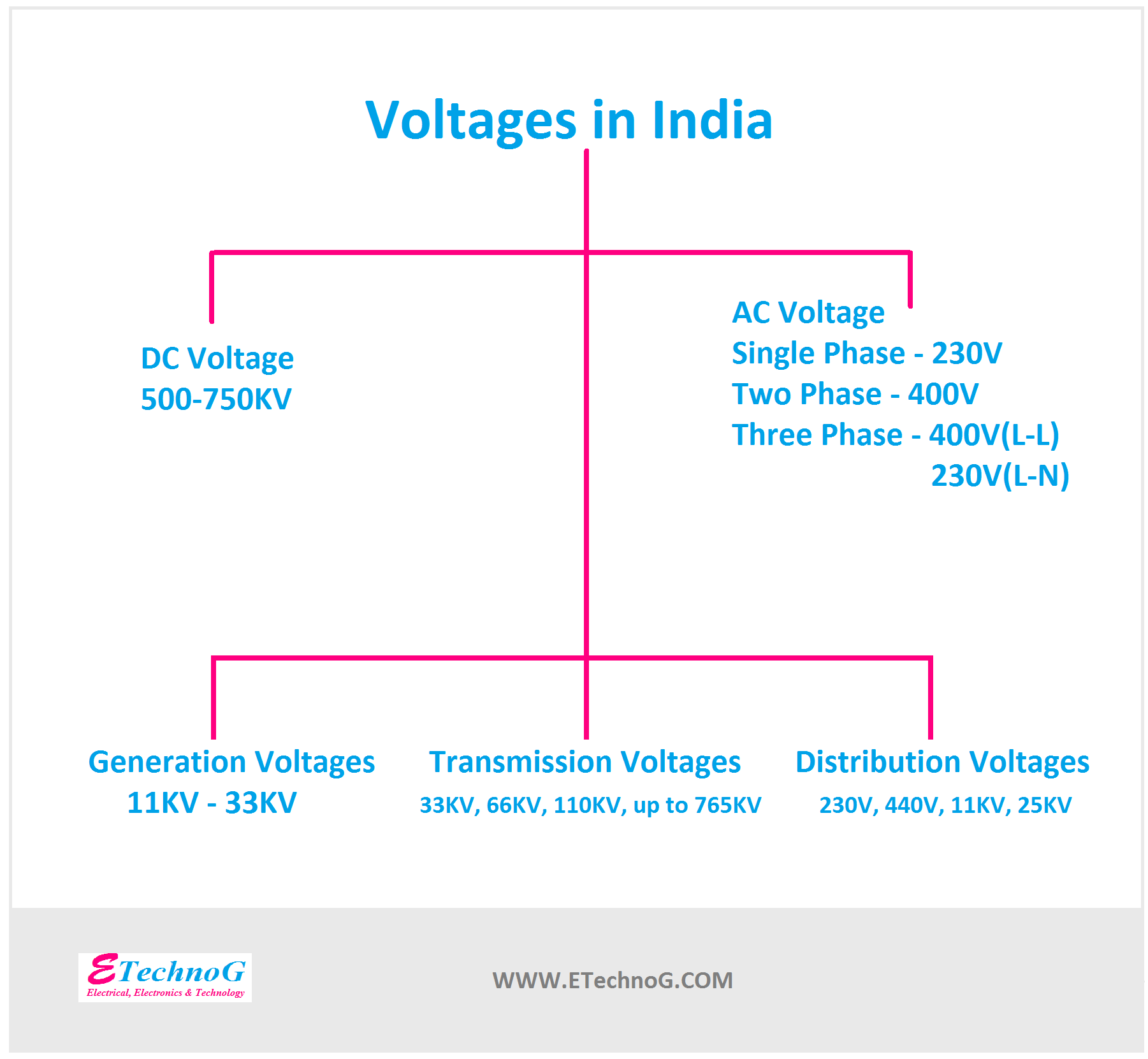
Classification of Voltages in India
The normal single-phase supply voltage in India is 230V. And the three-phase voltage in India is 400V. In this article, we are going to know all the classifications of voltage used for different purposes. First, of all let's know what is voltage. Voltage is the electrical pressure or potential difference across a conductor that forces the current to flow through that conductor from higher potential to lower potential. Voltage is measured in volts and it is symbolized by the English letter 'V'. So when we talk about 230V or 400V that implies that is 230 volts or 400 volts. Voltage is also measured in Kilo Volts(KV) and Mega Volts(MV). These are used for higher voltage levels.
DC Voltage in India
Nowadays, the DC generation is very rare in India. Nowadays it is generated for special purposes only and private use and that is limited up to 200V. But in older days the electrical power generation transmission completely depended on the DC. At that time the DC generation voltage in India was 500 to 750KV and the transmission voltage was 400 to 1000KV.
AC Voltage in India
Nowadays, in India, all the electrical power generation, transmission, and distribution depend on AC because it is very easy to generate, transmit, and convert. There are three types of voltage is used in India. That is explained below,
Single Phase Voltage
Generally, the standard single-phase voltage for India is 230V for domestic purposes. And it is used with a 50Hz frequency. As we know practically, electrical parameters are not constant they vary. It is seen that the voltage commonly varies from 220V to 240V. And frequency varies from +3% to -3% of 50Hz. Single-phase voltage is obtained from any one phase of the three-phase supply and the neutral. For domestic applications, single-phase supply is mostly used.
Two-Phase or Double Phase Voltage
Two-phase or Double-Phase is very rarely used. It is used when a high voltage is required with two phases or two terminals. It is obtained by taking any two-phase from a three-phase source. The standard two-phase voltage in India is 400V. Sometimes it goes up to 440V. This type of supply is required for high-power lighting, motor operation, power transmission, etc.
Three Phase Voltage
Three-phase is very popular in India. In fact, a three-phase system is used for power generation, transmission, and somewhere distribution. Single-phase and two-phase supplies are also taken from a three-phase source. The standard three-phase voltage in India is 400 V although it is varying up to 440V. This 400V is the phase-to-phase or line-to-line voltage and the phase-to-neutral voltage is 230V which is known as single-phase supply.
Electrical Power Generation Voltage in India
The common electrical power generation voltage in India is 11KV. But nowadays usually, it can be up to 33KV. The generation voltage indicates the voltage across the output terminal of the alternator in a power-generating plant. Generally, this voltage is increased by a step-up transformer for long-distance transmission.
Electrical Power Transmission Voltage in India
The common electrical power transmission voltages in India are 33KV, 66KV, 110KV, 132KV, 220KV, 400KV, 765KV, etc. You can see the transmission voltages are much higher than the generation voltages. Using step-up transformers or power transformers. The transmission voltages are multiplied by 11 because these voltages are easy to obtain with minimum losses.
Electrical Power Distribution Voltage in India
The common electrical power distribution voltages in India are 230V for single-phase power supply, and 400V for three-phase power supply. For special purposes such as 11KV is distributed to the industrial consumer and 25KV for the Traction system. Distribution voltages are lower than transmission so the step-down transformers or distribution transformers are used to decrease the transmission voltage.
Read Also:
- What is Electric Pole? Types, Applications, Advantages
- Line Capacitance and Earth Capacitance Effect in Transmission Line
- What is Line Trap or Wave Trap? Symbol, Circuit diagram
- Why DC Supply is used for Control Circuit in Substations, not AC?
- [Actual] Purpose and Function of Earth Wire in Transmission Line