List of Overvoltage Protection Device and Their Function
Overvoltage fault is very common and frequently occurs as an electrical fault. Overvoltage fault occurs when the voltage rises above the maximum limit voltage level of a circuit. According to the time duration, overvoltage faults can be divided into different types such as,
- Transient Voltage
- Surge Voltage
- Spike Voltage
- Permanent Overvoltage
Anyway, in this article, we are going to see the list of all overvoltage protection devices and their function, applications, and features.
Here, is the list of overvoltage protection devices,
- Arcing Horns
- Lightning Rod
- Spark Gap
- Lightning Arrester
- Surge Arrester
- Transient Voltage Suppression(TVS) Diode
- Metal oxide varistor
- Avalanche Diode
- Zener Diode
- Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs)
- Thyristor Surge Suppressors (TSS)
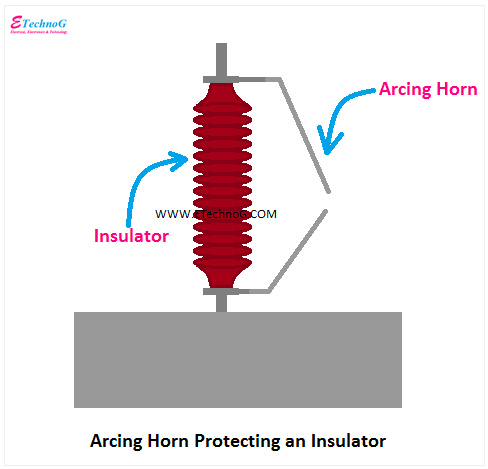
Arcing Horns for Overvoltage Protection
Arcing Horns or Arc-Horn are mostly used with insulators in overhead transmission lines and switching arrangements. Basically, an ARC horn has two projecting conductors very close to each other but not connected. Among these two conductors, one is connected to the live part of the power system and another is connected to the earth or ground. So, in normal conditions, no current flows through the ARC horn. But when a high voltage occurs in the power system an ARC is created between two projecting conductors of the ARC horn and it also creates a close path between the live part and the ground. So, current starts flowing from the live or phase to the ground through the ARC horn, and voltage will decrease.
Lightning Rod
Lightning Rod is also known as Lightning Conductor. Basically, it is a metal rod mounted or placed at the top of a building. The main function of a lightning rod is to protect the building from the heavy strike voltage due to lightning. When the lightning occurs near the building, it will hit the lightning rod and all the current will ground through that rod. The lightning rod system contains a metal rod mounted on the top of the building and a rod placed on the ground. These two rods are connected by an earth wire.
Spark Gap
The spark gap is almost similar to an ARC horn. Here, also two conductors are placed nearly to each other and this arrangement is placed in a closed area filled with any gas or air. When the voltage between the two conductors exceeds the breakdown voltage of the filled gas, it got ionized fully. Once the gas is ionized, the resistance will decrease and electric current starts flowing through it. So, this is also connected between the live part of a power system and the ground or earth.
Lightning Arrester
The main function of a Lightning Arrester is to arrest the lightning and give protection against overvoltage produced by lightning. Lightning arresters are mostly used in electrical power transmission systems through overhead lines and telecommunication systems. A lightning arrester has a high voltage terminal that is connected to the live part of the power system and a low voltage terminal connected to the ground or earth. So, when a surge voltage occurs due to the lightning or switching, the lightning arrester diverts the flow of current from the live part to the ground. So, the surge voltage is minimized quickly.
Zener Diode for Overvoltage Protection
A Zener diode can be used for overvoltage protection in sensitive electronic circuits. A Zener diode is a special type of diode that is designed to operate in the reverse bias or reverse breakdown region, which means it can conduct current when a certain reverse voltage, known as the Zener voltage (VZ), is applied across its terminals. To use a Zener diode for overvoltage protection, it is typically connected in parallel with the circuit or component that needs to be protected. When the voltage across the Zener diode reaches or exceeds its Zener voltage, it begins to conduct heavily and ground the excessive current which effectively clamping the voltage to the Zener voltage.
Read Also: