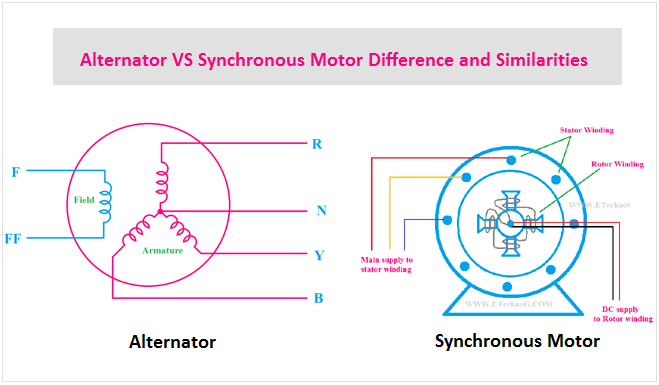
Alternator VS Synchronous Motor Difference and Similarities
The main difference between Alternator and Synchronous motor is an alternator is an electricity-generating machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating nature whereas a synchronous motor is an electricity-consuming machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
There also some similarities between Alternator and synchronous motor that are,
- The alternator and Synchronous motor both are AC machines and they are designed to work with an AC power supply.
- The alternator and synchronous motor both require a DC supply to their field winding for their operations.
- The alternator and synchronous motor both rotate at synchronous speed.
The main key differences between alternator and synchronous motor are,
(1) The alternator always rotates at a constant speed as it is connected to a prime mover, so when the speed of the prime mover changes, the speed of the alternator also be changed. On the other hand, a synchronous motor can rotate at variable speed as its speed depends upon the supply voltage, frequency, and power factor.
(2) Synchronous motor is not self-starting. On the other hand, the starting and running of the alternator both depend upon the prime mover.
(3) Synchronous motors are mainly used for power factor control or power factor correction purposes. Also somewhere they are used to drive mechanical loads. Alternators are used to generate electricity in power generation plants and automobiles for battery charging.
(4) A Synchronous Motor is an electrical load that consumes electrical power whereas the alternator is an electrical power-generating device that generates electrical energy by the conversion of mechanical energy.
(5) The power factor of the alternator depends upon the type of load connected to it, if an inductive load is connected then the power factor will be lagging, if a capacitive load is connected then the power factor will be leading, if a resistive load is connected then the power factor will be unity. On the other hand, the power factor of the synchronous motor depends upon the applied DC power supply to its rotor field coil.
(6) Synchronous Motor Provides a function to vary the power factor manually by varying the DC voltage applied to its rotor field coil but in the case of an alternator, there is no facility to vary the power factor manually.
(6) Synchronous Motor Provides a function to vary the power factor manually by varying the DC voltage applied to its rotor field coil but in the case of an alternator, there is no facility to vary the power factor manually.
(7) The operating frequency of the alternator can be changed by changing or varying the speed of the rotation of the rotor. That is why, in every real application of the alternator speed of the alternator is a very important factor. A constant speed is always maintained by the maintaining of the speed of the prime mover.
Generally, in a power generating station, multiple alternators are connected in parallel and they synchronize to each other. Frequency is a very important factor of the synchronization. Any changes in the frequency can disconnect the alternator from the parallel operation. On the other hand, a synchronous motor always runs with a constant frequency that the input power supply has. There are no features or ways to change the operating frequency of the synchronous motor.
Read Also:
- [Explained] Motor Circuit Protection System and Devices
- Actual Difference between Servo Motor and Stepper Motor
- Actual Difference Between Synchronous Motor and Induction Motor
- AC Motor VS DC Motor | Difference with Advantage and Disadvantage
- Applications and Advantages of all types of Motor- DC Motors, AC motors, Universal Motors