What is Oscillator? Types and applications of Oscillator
Oscillator Definition, Types, and Applications
An Oscillator is an electronic circuit or device that can convert a steady-state signal into an oscillating signal. For example, the oscillator can convert a steady-state DC signal into a periodic AC signal of the desired frequency.
There is a huge application of Oscillator in electronics engineering and also it is widely used in electrical engineering. Actually, the oscillation is not only related to electrical or electronics, but there is a mechanical oscillator also available. So if we look at the common definition of an oscillator then we see,
Definition of Oscillator: The oscillator is a device(may be electrical or maybe mechanical) which can create oscillation of steady-state energy(maybe electrical energy or mechanical energy).
As we represent the electrical energy by the electrical or electronic signal and waveforms theoretically that is why we used the word Signal instead of energy in the definition of an electronic oscillator.
As I said before that an electronic oscillator converts the steady state signal into an oscillating signal, but Why we need Oscillating signal?
You may know that we have needed the signals of different different frequencies for different different applications like in digital electronics most of the devices like Flip-Flop circuits, Registers etc need a clock pulse for their operation. The clock pulse or clock signal is nothing but an oscillating signal. Even the CPU of the computer needs a clock pulse. As the oscillating signals have a frequency that is why they are used for many applications. We will discuss the more applications later.
How Oscillator Works?
The concept of a simple oscillator circuit:
The basic concepts of an oscillator can be given by a simple electrical circuit which consists of a capacitor and an inductor connected in parallel. But remember that you must have the basic knowledge of Inductor and Capacitor to understand that circuit. We know that the capacitor store the electrical energy in the form of charge and the inductor can also store electrical energy but in the form of an electromagnetic magnetic field.
As you see in the above figures a capacitor and an inductor are connected in parallel. Assume the capacitor is fully precharged, so now the capacitor starts discharging through the inductor, and the electrical energy is stored into the inductor in the form of an electromagnetic field. When the capacitor is fully discharged there will be no current flow in the circuit. In this condition, the capacitor is fully discharged and the inductor is fully charged.
Now the inductor starts discharging through the capacitor and the capacitor starts charging in the opposite polarity. So this charging and discharging of the capacitor and inductor makes the oscillating signal or we can say the repeatable get and paid of electrical energy between the capacitor and inductor creates the oscillations.
You may have a question in your mind how long it runs? The inter-conversion of energy cannot continue forever because of energy losses. The energy loss will occur due to the resistance of the circuit. For this reason, the oscillation becomes decreasing and a time will come when the oscillation will be zero.
So a simple oscillator circuit can be made by capacitor and inductor but it cannot give the continuous oscillation and of constant amplitude.
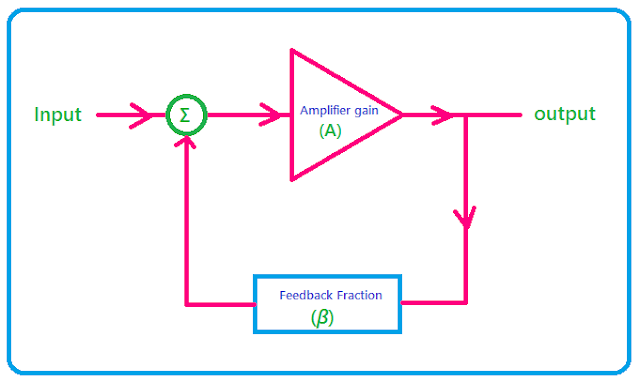
Oscillator circuit using Amplifier:
The oscillator circuit can be made by an amplifier with feedback. The feedback may be positive or regenerative. The feedback means a part of the output signal of the amplifier is fed back to the input of the amplifier. The oscillator circuit using an amplifier can give continuous constant amplitude oscillations.
So when we applied some sinusoidal signal as the input of the amplifier the output of the amplifier will be the multiplication of the gain of the amplifier and the input signal. Now the output of the amplifier is given to the feedback circuit as the input. Generally, the feedback circuit is nothing but a frequency-selective circuit or resonant circuit and it decides what fraction of the output signal of the amplifier is to be given to the input of the amplifier as feedback signals.
When the output signal of the feedback circuit is added to the input signal and at the same time the input signal of the amplifier is removed the feedback signal will act as the input of the amplifier. Now after removing the input signal, we can decide which type of oscillation(sustain or not) we want to get and this depends upon the multiplication of the gain of the amplifier and the feedback fraction of the feedback circuit.
So from the above explanation, it is cleared that the input of the oscillator circuit does not need all over the time during the operation of the oscillator. The input is needed only for starting the oscillation and once the oscillation is started the input can be removed or in other words, the oscillator can give the output without input.
Types of Oscillator:
(1) We already know that the oscillator circuit has a feedback path so according to the feedback path,
1. Positive Feedback Oscillator
2. Negative Feedback Oscillator
(2) We know that the Oscillator circuit creates an oscillating signal which may be many types in Waveform. So based on the types of waveform the Oscillator is classified as below,
1. Sine Wave Oscillator
2. Rectangular or square wave Oscillator
3. Sawtooth Wave oscillator
A special type of single Oscillator can also create all types of Waveforms.
(3) Based on the circuit design,
1. LC Oscillator
2. RC Oscillator
3. Crystal Oscillator
(4) According to the frequency range,
1. Low-Frequency Oscillator
2. High-Frequency Oscillator
3. Very High-Frequency Oscillator
4. Ultra High-Frequency Oscillator
Examples of Oscillators:
Some examples of oscillators are the Royer Oscillator, Tri-tet Oscillator, Armstrong Oscillator, Meissner Oscillator, Pierce Oscillator, Ring Oscillator, etc.
Applications of Oscillator:
There are huge applications of oscillators which are given below,
1. The oscillator is used in Watches.
2. Oscillators are used in Radio Circuits.
3. Oscillators are used in smartphones, computer laptops, etc.
4. Royer Oscillators are used in some DC to AC Inverter circuits.
5. The Armstrong Oscillator is used for very high-frequency sinusoidal signals.
6. Pierce Oscillators are mainly used in crystal oscillator circuits.
7. Oscillators are used in stun guns.
8. Oscillators are used in ultrasonic machines.
9. In metal detectors oscillators are also used.
Read Also:
Thank you for visiting the website. keep visiting for more updates.
What is Oscillator? Types and applications of Oscillator
 Reviewed by Author
on
January 24, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Author
on
January 24, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Author
on
January 24, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Author
on
January 24, 2019
Rating: